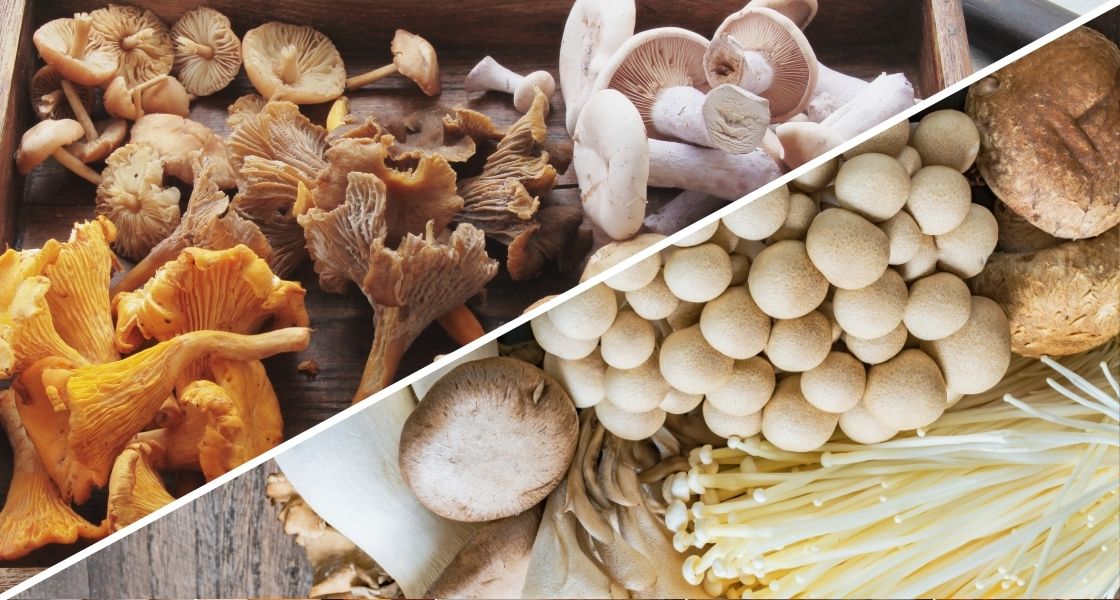
In the culinary world, mushrooms stand out for their distinctive flavors and textures, but not all mushrooms are created equal. This article explores the nuances between two primary sources: mushrooms - wild or cultivated? Delving into aspects from nutritional content to environmental impact, we compare these two methods to understand not only their culinary differences but also their broader implications on health and the environment. Whether you are a gourmet chef, a home cook, or simply a mushroom enthusiast, this comparison will provide valuable insights into the fascinating world of fungi.
The nutritional differences between wild-caught and cultivated mushrooms
Wild-caught mushrooms often grow in diverse, natural ecosystems, which can influence their nutritional content. Wild mushrooms UK based typically access a wider range of nutrients from the soil compared to their cultivated counterparts. Cultivated mushrooms, grown in controlled environments, have a consistent nutrient profile, beneficial for those seeking predictable dietary content. Both types provide essential vitamins and minerals, although the exact levels can vary significantly depending on the species and growing conditions.
Popular varieties of mushrooms in wild and cultivated categories
Exploring the world of fungi reveals a rich diversity of mushrooms, each with unique flavors and uses. Here are some of the most popular mushroom types found in both wild and cultivated environments:
Wild mushrooms (UK most popular):
- Chanterelles, known for their golden color and fruity aroma, are another favorite among foragers.
- Porcini mushrooms, celebrated for their robust flavor, are a cherished find in wooded areas during the autumn months.
- When it comes to cultivated mushrooms, the white mushroom dominates due to its versatility in cooking and mild taste.
- Portobello mushrooms, are prized for their meaty texture, making them a popular choice for grilling.
- Shiitake mushrooms, cultivated on hardwood substrates, are cherished for their bold, savory flavor and are a staple in many Asian cuisines.
Environmental impacts of harvesting wild-caught mushrooms versus cultivating them
The harvesting of wild-caught mushrooms, for example types growing in forests, can have minimal environmental impact when done sustainably, preserving biodiversity and the natural ecosystem. However, overharvesting poses significant risks, including the disruption of local flora and fauna. On the other hand, mushroom cultivation is typically more controlled but can require significant resources such as water, energy, and space. Innovative farming techniques, such as vertical farming are reducing the ecological footprint of mushroom cultivation. Both methods, if managed responsibly, offer sustainable ways to meet the growing demand for mushrooms.
Flavor profiles of wild-picked mushrooms compared to those grown in farms
Wild-caught mushrooms are celebrated for their complex and varied flavor profiles, often possessing a depth and intensity that mushrooms in cultivation typically lack. Foragers and chefs alike treasure wild varieties like boletes and chanterelles for their earthy, nutty, and sometimes fruity notes, which can vary significantly depending on their natural habitat and the soil they grow in. In contrast, cultivated mushrooms, such as the common white button, shiitake and portobello, offer a more consistent taste due to the controlled conditions of their growth environments. These mushrooms tend to have a milder flavor, making them versatile in a wide range of dishes. While they lack the distinctive wild taste, cultivated mushrooms are crucial for everyday culinary use due to their availability and uniformity.
Culinary applications of wild and cultivated mushrooms
The use of mushrooms in the kitchen varies significantly between wild and cultivated types, each bringing its unique flavors and textures to dishes. Wild-caught mushrooms, such as boletes, porcini, and chanterelles, are highly prized in gourmet cooking for their robust and distinctive tastes. These varieties excel in dishes where their flavors can stand out, like in risottos, sautés, and creamy sauces. On the other hand, cultivated mushrooms such as white button, portobello and shiitake are staples in everyday cooking due to their consistency and milder flavors. They are incredibly versatile, ideal for a wide range of culinary uses from simple stir-fries to complex marinades. Both wild and cultivated mushrooms offer a wealth of options for chefs and home cooks alike, each enhancing the dishes they are used in with their unique characteristics.